by PushtoLearn
Was/were – past simple of ‘be’
Table of Contents
Was vs Were Exercise
This exercise focuses on Was vs Were
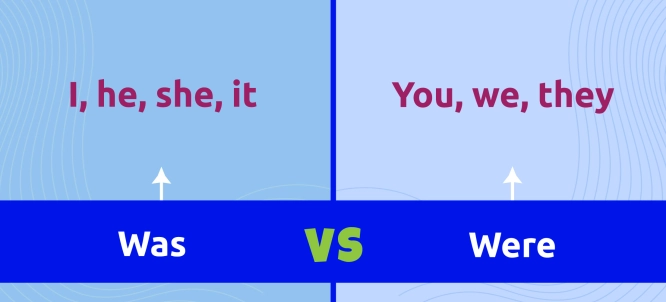
When to Use "Was" and "Were"
The choice between "was" and "were" depends on the subject of the sentence:
-
Was is used with I, he, she, it (singular subjects).
-
Were is used with you, we, they (plural subjects and "you" in both singular and plural form).
Examples:
|
Subject |
Past Form of Be |
Example |
|
I |
was |
"I was at home yesterday." |
|
He / She / It |
was |
"She was very happy." |
|
You |
were |
"You were late to class." |
|
We |
were |
"We were on vacation." |
|
They |
were |
"They were excited." |
Using "Was" and "Were" in Positive Sentences
For positive statements in the past, use "was" or "were" depending on the subject.
-
Examples:
-
"I was tired after work."
-
"He was a great teacher."
-
"They were at the party last night."
-
"We were in Paris last summer."
Using "Was" and "Were" in Negative Sentences
To make negative sentences, add "not" after "was" or "were." You can also use the contractions "wasn’t" (was not) and "weren’t" (were not).
-
Examples:
-
"I was not (wasn’t) ready for the test."
-
"She wasn’t at home last night."
-
"They were not (weren’t) interested in the game."
-
"We weren’t happy with the result."
Using "Was" and "Were" in Questions
To form questions, start the sentence with "was" or "were," followed by the subject.
-
Examples:
-
"Was she at the meeting yesterday?"
-
"Were you in class this morning?"
-
"Was it raining yesterday?"
-
"Were they friends in college?"
Examples in Context
-
Positive Sentence: "He was a doctor."
-
Negative Sentence: "They weren’t at the park yesterday."
-
Question: "Were you awake when the alarm rang?"
Quick Reference Table
|
Sentence Type |
With "Was" |
With "Were" |
|
Positive |
"She was a good student." |
"They were on time." |
|
Negative |
"I wasn’t feeling well." |
"We weren’t late." |
|
Question |
"Was he at work yesterday?" |
"Were you there last week?" |
Common Mistakes with "Was" and "Were"
-
Using "was" with plural subjects:
-
Incorrect: "They was happy."
-
Correct: "They were happy."
-
Using "were" with singular subjects like "I":
-
Incorrect: "I were at the store."
-
Correct: "I was at the store."
-
Forgetting to use contractions in spoken English:
-
In spoken English, it’s common to use "wasn’t" and "weren’t" instead of "was not" and "were not."
FAQ
Can I use "were" with "I"?
No, "I" always goes with "was" in the past simple (e.g., "I was at the concert").
Is "wasn’t" the same as "was not"?
Yes, "wasn’t" is just a contraction of "was not." It’s more commonly used in spoken English.
Can I use "was" and "were" for things, not just people?
Yes, "was" and "were" can describe the past state of things, animals, places, etc. For example, "The book was interesting."
When do I use "was" or "were" for questions?
Start the question with "was" or "were" (e.g., "Was she happy?" or "Were they late?").
What’s the difference between "were" and "we’re"?
"Were" is the past form of "be" for "you/we/they," while "we’re" is a contraction for "we are."

