by PushtoLearn
Future forms – will, be going to, present continuous
Table of Contents
Future Forms – Will, Be Going To, Present Continuous - Exercises
These exercises focus on Future Forms – Will, Be Going To, Present Continuous
Future with "Will"
"Will" is used to express decisions made at the moment of speaking, predictions, promises, offers, and future facts. Learn more about Future Simple.
Structure:
Subject + will + base verb
Uses:
-
Decisions made now:
-
"I will call her right away."
-
Predictions (based on opinion):
-
"I think it will rain tomorrow."
-
Promises or offers:
-
"I will help you with your homework."
-
Facts about the future:
-
"The sun will rise at 6 a.m."
Examples:
-
"She will finish the project tomorrow."
-
"Don’t worry, I will take care of it."
-
"I will always love you."
-
"Don’t worry, I will call you later."
-
"People will live on Mars one day."
-
"She will win the race."
-
"Oh no, the phone is ringing. I will answer it!"
-
"We don’t have any milk. I will go buy some."
-
"That looks heavy. I will help you."
-
"I will make us some coffee."
-
"You will get wet if you don’t take an umbrella."
-
"He will be angry if you’re late again."

Future with "Be Going To"
"Be going to" is used to express plans or intentions made before speaking and predictions based on evidence.
Structure:
Subject + am/is/are + going to + base verb
Uses:
-
Plans or intentions (already decided):
-
"I am going to visit my grandma next weekend."
-
Predictions based on evidence:
-
"Look at those clouds! It is going to rain soon."
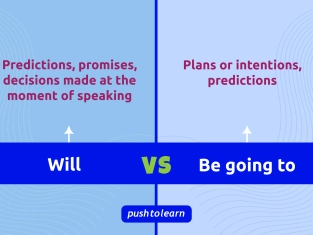
Have a look at the difference between Will vs Be going to.
Examples:
-
"We are going to travel to Spain this summer."
-
"The baby is going to cry; she looks upset."
-
"We’re going to travel to Spain next summer."
-
"She’s going to study medicine at university."
-
"I’m going to start a new job next week."
-
"He’s going to fall off the bike! He’s not looking!"
-
"That dog is barking loudly. It’s going to attack!"
-
"They’re going to be late. The bus hasn’t arrived yet."
Future with Present Continuous
The present continuous is used to talk about fixed plans or arrangements in the near future, often with a specific time mentioned.
Structure:
Subject + am/is/are + verb-ing
Uses:
-
Definite plans or arrangements:
-
"I am meeting my friend at 5 p.m."
-
"She is flying to New York tomorrow."
Examples:
-
"We are having a party this Saturday."
-
"He is taking the train at 8 a.m."
-
"I’m meeting my friend at 5 p.m."
-
"She’s flying to London tomorrow."
-
"We’re having dinner with our parents tonight."
-
"He’s starting his new job next Monday."
-
"They’re attending a conference next week."
-
"I’m taking an English test on Friday."
-
"We’re leaving for the airport at 6 a.m."
-
"He’s driving to New York this weekend."
-
"I’m going home after class."
Refresh your knowledge about Present Continuous.
Comparing the Future Forms
|
Form |
Use |
Example |
|
Will |
Immediate decisions, predictions, promises |
"I will call you tomorrow." |
|
Be Going To |
Planned intentions, evidence-based predictions |
"I am going to study medicine." |
|
Present Continuous |
Definite plans, arrangements |
"We are meeting at the café at 6 p.m." |
Common Mistakes
-
Using "will" for plans instead of "be going to" or present continuous:
-
Incorrect: "I will go to the store later."
-
Correct: "I am going to the store later."
-
Mixing "will" and "be going to" incorrectly for predictions:
-
Use "will" for general predictions: "It will be cold tomorrow."
-
Use "be going to" for predictions based on evidence: "Look at the sky; it is going to rain."
-
Using the present continuous for uncertain plans:
-
The present continuous is for definite plans, not general intentions:
-
Incorrect: "I am buying a new car someday."
-
Correct: "I am going to buy a new car someday."
FAQ
Can I use "will" and "be going to" interchangeably?
Not always. Use "will" for decisions made on the spot or general predictions. Use "be going to" for plans or predictions based on evidence.
How is the present continuous different from "be going to"?
The present continuous emphasizes fixed plans or arrangements, often with a specific time mentioned, while "be going to" is for intentions or general plans.
Can I use "will" for formal arrangements?
No, use the present continuous for formal arrangements: "We are meeting the manager at noon."
Do these forms work with all subjects?
Yes, "will," "be going to," and the present continuous can be used with any subject, but make sure the verb matches the subject in number (e.g., "I am," "they are").
Which form is more common in casual speech?
In casual speech, "be going to" is commonly used for plans, and "will" is often used for quick decisions and promises.